Valium Mechanism Of Action
If you're looking for video and picture information linked to the keyword you have come to pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, hunt and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
includes one of thousands of movie collections from various sources, especially Youtube, so we recommend this video for you to see. This site is for them to stop by this website.

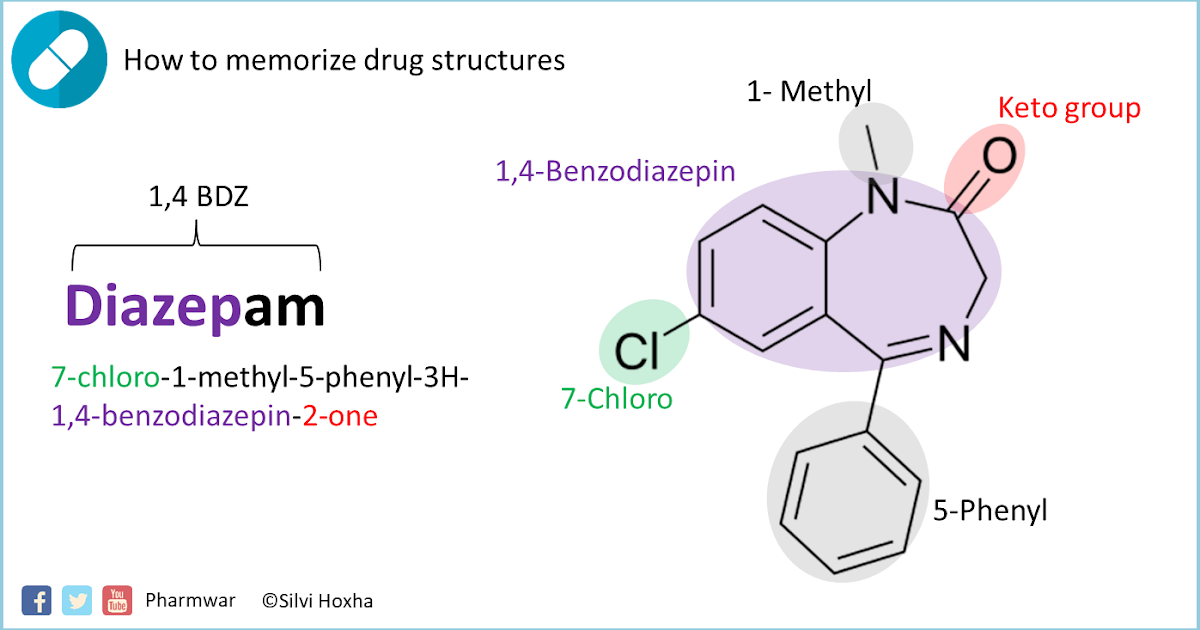
Benzodiazepines such as diazepam bind to receptors in various regions of the brain and spinal cord.
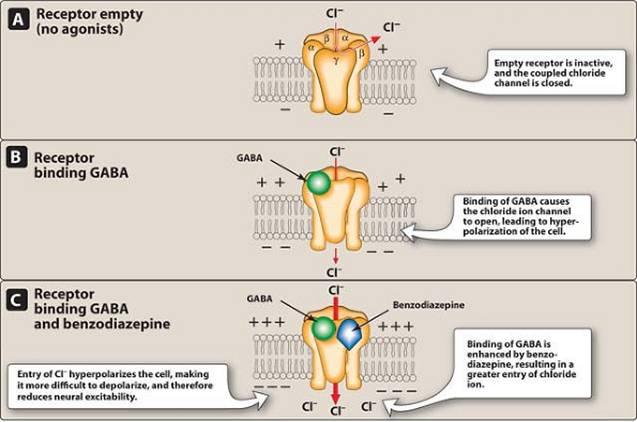
Valium mechanism of action. Diazepam is a benzodiazepine. The GABA A receptor is an inhibitory channel which when activated decreases neurologic activity. The presumed mechanism of action of diazepam and other benzodiazepines in the central nervous system is by potentiation of the inhibitory effect of g-aminobutyric acid on neuronal transmission. All benzodiazepines cause a dose-related central nervous system depressant activity.
Diazepam is very lipid-soluble enters the brain rapidly and may have an anticonvulsant effect within a minute after intravenous administration. 47 All benzodiazepines have hypnotic anticonvulsant muscle relaxant amnesic and anxiolytic properties. Its action is further prolonged by the even longer half-life of 2-5 days of its principal active metabolite desmethyldiazepam nordiazepam the relative proportion of which increases in the body on long-term administration L5188. Diazepam is used recreationally as a sedative or to enhance the effects of alcohol or opioids.
This increases binding of GABA gamma-aminobutyric acid a powerful inhibitory neurotransmitter present in the Central Nervous System CNS How fast does the Valium work. Mechanism of action Diazepam is a benzodiazepine that binds to a specific subunit on the GABA A receptor at a site that is distinct from the binding site of the endogenous GABA molecule. GABAs functions include CNS involvement in sleep induction. Diazepam affects Type A GABA receptors through positive allosteric modulation.
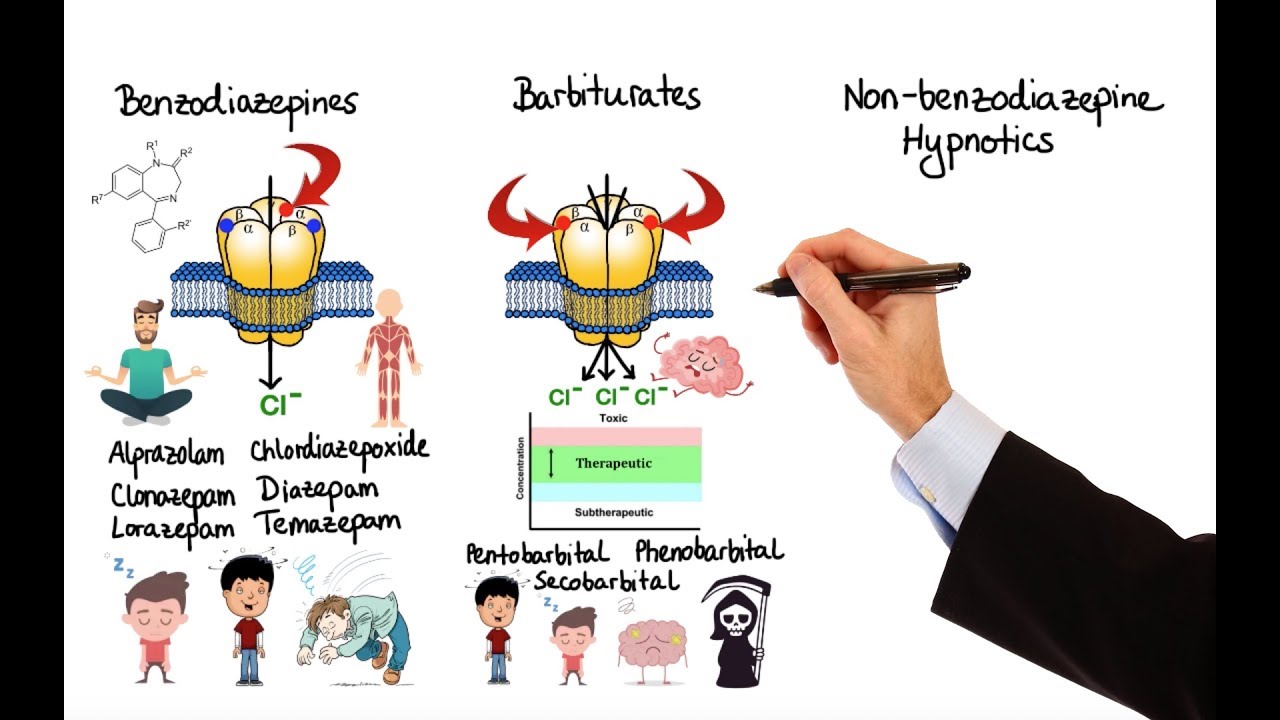
Commonly prescribed doses are 540 mg daily. The plasma half-life. Mechanism of action Benzodiazepines bind to gamma-aminobutyric acid type A GABAA receptors which are responsible for most of the inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system and. Mechanisms of action refer to the method by which benzodiazepines act when they reach the brain and make changes in psychological functioning.
Alcoholism weighs down on the brain such that the neurotransmitters are rewired and the body cannot function without alcohol. Diazepam is a benzodiazepine tranquilliser with anticonvulsant sedative muscle relaxant and amnesic properties 9106. They are known pharmacologically as GABAergic agents sedative-hypnotics or minor tranquilizers. This causes severe withdrawal symptoms which can cause harm to the affected party.
Use extreme care when administering diazepam in patients with limited pulmonary reserve or compromised respiratory function related to concurrent pulmonary disease process eg asthma pneumonia or neurologic damage due to the possibility of apnea or cardiac arrest. It may also be used to cause memory loss during certain medical. This binding increases the inhibitory effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA 9106. Valium Mechanism Of Action.
Diazepam has a biphasic half-life with an initial rapid distribution phase followed by a prolonged terminal elimination phase of 1 or 2 days. Benzodiazepines presumably exert their effects by binding at stereo specific receptors at several sites within the central nervous system. Diazepam has been used for treating alcohol dependence in alcoholics. Valium - Clinical Pharmacology Diazepam is a benzodiazepine that exerts anxiolytic sedative muscle-relaxant anticonvulsant and amnestic effects.
A tranquilizer trade name Valium used to relieve anxiety and relax muscles. Grab our free cheatsheet covering the 50 most commonly prescribed medications right here. Most of these effects are thought to result from a facilitation of the action of gamma aminobutyric acid GABA an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Benzodiazepines act directly on an inhibitory neurotransmitter of the brain Known as Gamma butyric acid GABA binding to specific receptors of this neurotransmitter and acting as a GABA agonist.
Oral diazepam tablets are contraindicated for use in patients with severe respiratory insufficiency or sleep apnea syndrome. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions including anxiety seizures alcohol withdrawal syndrome benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome muscle spasms trouble sleeping and restless legs syndrome. Diazepam is a central nervous system depressant that has numerous medical uses. Acts by enhancing the inhibitory actions of the neurotransmitter GABA.
Induction with diazepam is characterized by hemodynamic stability. Can also be used as an anticonvulsant drug in cases of nerve agent poisoning. Increased binding of GABA to its receptors takes either 1-5 minutes or up. Thought to result from a facilitation of the action of gamma aminobutyric acid GABA an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
Sedation for procedures Muscle Spasms. Diazepam on the other hand works on calming the brain and the nerves. Nevertheless it redistributes to many tissues and its CNS effect declines in 20 to 30 minutes so longer-acting anticonvulsants should be used concomitantly to prevent recurrent seizures or SE.