What Does Va Rating Mean On A Transformer
If you're searching for video and picture information related to the key word you have come to visit the right blog. Our website provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, hunt and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
includes one of thousands of video collections from various sources, especially Youtube, therefore we recommend this movie that you view. This site is for them to stop by this website.

A volt-ampere SI symbol.
What does va rating mean on a transformer. For a typical 24 volt secondary this is simply using watts law to calculate amperage. Well the wire we use to connect the CT has some resistance to it. In many circumstances the power required by the load is equivalent to the rating of the transformer expressed in either VA or kVA. CTs with larger cores are generally capable of transferring more power.
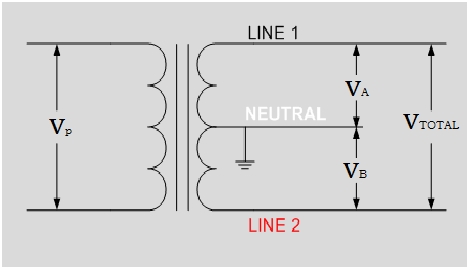
The fuse must be smaller than the VA rating of the transformer. It shows the maximum value of the voltage at which the machine is designed and the current consumption occurs at that voltage. The VA rating refers to the power distribution rating relative to how much power the transformer can deliver to the load. Sometimes a voltage transformer may have two or more than two secondary cores.
The VA rating is the maximum that the transformer concerned can SAFELY supply without over heating. For example a 1KW 1000 Watts load would require a 1kVA transformer unity power factor. The VA rating is used to select the properly sized fuse for that circuit. It is a heart of power systems.
Simply put the VA rating is the math formula used in determining the amperage at a given voltage. In direct current DC circuits this product is equal to the real power in wattsVolt-amperes are usually used for analyzing alternating current AC circuits. KVA stands for Kilovolt-Ampere and is the rating normally used to rate a transformer. The VA specification is also used in alternating current AC circuits but it is less precise in this application because it represents apparent power which often differs from true power.
To calculate VA you need to know the supply voltage and the current delivered to the load. The Voltage supplied by the transformer is just that - a supply Voltage of 16 V. Transformer capacity is rated in Volt-Amps VA which is generally the same as wattage Watts. To compute a loads VA requirements multiply its rated voltage Volts by its rated current Amps.
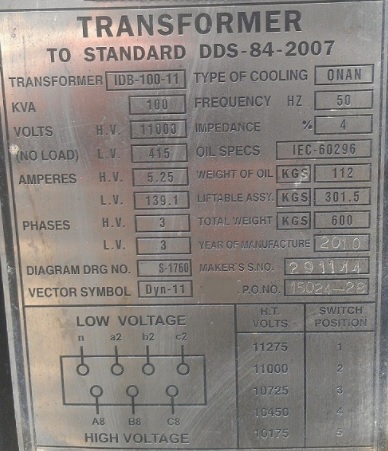
40 24 1666666 round up to 167 already So you cannot place more than 167 amps of constant load on the transformer without overloading it. Hence the transformer is rated by the VA only. To calculate the rating of the transformer for both single phase and three phase the load required to be fed and voltage at which load is to be fed must be known or should be calculated. The rating of transformer is given in terms of its kVA HVLV voltage and phase rotation for three phase transformer.
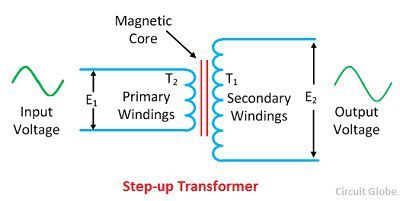
Transformers are static equipment which is used to convert the voltage or current to the different levels. The VA rating of the unit is similar to the circuit breakers in your home that protect you from overloads most breakers are 15amp breakers meaning that you should not ever plug in enough devices to use more then 15 amps of power or the breaker will trip and disconnect the load. A 40 VA transformer is rated for 40 VA or Volt-Amps on the secondary. But as per standard only some specific VA ratings are available in the market.
The size of a transformer is determined by the kVA of the load. If we are outputting current one might wonder why we care about power. Volt-ampere VA is a measurement of power in a direct current DC electrical circuit. In a DC circuit 1 VA is the equivalent of one watt 1 W.
These ratings are 10 25 50 75 100 150 200 and 500 VA for each single phase unit. This will then determine the maximum load that can be connected to the transformer. Theoretically we can design a voltage transformer with any VA output. The unit of apparent power is VA Volt-Amp.
The total deliverable apparent power is the rating of the transformer. You get the supply voltage from the voltage specifications associated with the primary and secondary windings. But the alternator and the transformer are the only machines which are rated in volt-amp VA. VA or V A.
Most loads are labeled with their proper operational voltage Volts current Amps frequency Hz and wattage Watts or VA. The machines are always rated in watts. Also VA is the unit used for the apparent power in an electrical circuitThe apparent power equals the product of root mean square voltage and root mean square current.